Introduction to Stock Dividends
In the world of trading and investing, stock dividends are generally considered to be a hallmark of stable and profitable companies. They are also a focus of retired investors hoping to generate sufficient income from their investments to support their lifestyle.
Many investors look to stock dividends to give them a profitable edge, but how do dividends work and are stocks that pay dividends really better investments than stocks that do not? In this article, we will explore a variety of trading strategies centered around dividends to determine their effectiveness and potential benefits.
By backtesting these strategies on historical stock data, we aim to provide insights on whether dividend yields, dividend growth, and monthly dividend payments can serve as valuable criteria for evaluating and selecting stocks. Join us as we dive deep into the realm of dividend stocks and uncover the strategies that may help you enhance your edge in the stock market.
Understanding Stock Dividends and How They Work
How stock dividends work
Dividend stocks are companies that distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. Dividends are usually paid in cash but can also be distributed as additional shares of stock through a dividend reinvestment scheme.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how dividend stocks work:
- Company earnings:
The company generates revenue through its business operations, and after accounting for expenses, taxes, and other costs, it (hopefully) retains some profit, also known as net income or earnings. - Board of directors’ decision:
The company’s board of directors decides how much of of the business’s earnings to reinvest in the business and how much to distribute as dividends to shareholders. - Declaration of dividends:
The board of directors declares the dividend to the market and specified the amount of the dividend to be paid per share, the record date and the payment date. The record date is the cut-off date for determining which shareholders will receive the dividend. The payment date is when the dividend is actually paid to shareholders. - Ex-dividend date:
The ex-dividend date is typically set two business days before the record date. On this date, the stock starts trading without the dividend and any buyers of the stock after this date will not be eligible to receive the dividend. On the ex-dividend date, the stock price usually drops by an amount roughly equal to the dividend payment because the new buyers will not receive the dividend and so are not willing to pay as much for the stock as buyers the previous day who were eligible to receive it. - Dividend payment:
On the payment date, the company distributes the dividends to shareholders, either as cash / cheque / wire transfer, or as additional shares of stock in the case of a dividend reinvestment plan - Dividend reinvestment:
Some companies offer Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) that allow shareholders to automatically reinvest their cash dividends back into additional shares of the company’s stock (sometimes at a small discount). This can help shareholders take advantage of the power of compounding and accelerate the growth of their investment over time, however it does also increase your exposure to the stock so may go against the principles of diversification, so keep that in mind too.
Investing in dividend stocks is a way to generate passive income, however as with any investment it is only part of the story. You also need to take into account the capital growth of the stock you are holding – In my opinion it does not make sense to hold a falling stock just to collect a small dividend. That feels like picking up pennies in front of a steamroller to me 😉.
Stock Dividend Calculation
When performing a stock dividend calculation there are several factors to consider:
- Company earnings per share
- Dividend payout ratio
- Stock price
- Dividend yield
Dividends are paid out of a stock’s earnings. So the first factor to understand is the earnings per share. The earnings per share is calculated by dividing the total earnings by the number of shares outstanding.
The dividend payout ratio is the percentage of company earnings that the board decides to pay as a dividend. For example, a company with a dividend payout ratio of 0.25 would pay 25% of it’s earnings per share as a dividend. The higher this number, the more of a company’s earnings are being paid to shareholders as a dividend and the less the company is retaining to invest in future growth.
The stock price is important from the investor’s perspective because it determines how much we are paying for the earnings or dividend of the stock. If the dividend is $0.1 per share on a $5 stock that is much more attractive than if the stock price was $10 assuming no change in the share price.
This is where the dividend yield comes in – the dividend yield is the annual dividend as a percentage of the stock price. For example a stock that pays an annual dividend of $0.1 with a stock price of $5 has a dividend yield of 2% ($0.10 / $5.00 x 100)
Stock Dividend Listing
Investors can find stock dividend listings in a variety of places online including:
- financial news websites and stock screeners (eg. Yahoo Finance)
- Brokerage platforms (Most brokers provide stock screeners for their clients use)
- Dividend focused websites (eg. com)
- Company websites (Go to the investor announcements section)
If you are an active stock trader like me then you can also get the stock dividend data along with the historical share prices from Norgate data so that you can build dividends into your historical trading system backtests to ensure you understand the total return of your trading strategy.
Highest Dividend Stocks: Which stocks pay the highest dividends
This highest dividend-paying stocks are typically businesses that have very stable earnings with relatively modest potential for growth through reinvestment, or stocks that are required to distribute most of their income to investors. As a result, highest dividends are generally paid by:
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): In the United States the IRS requires REITs to pay out 90% or more of their taxable profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. This results in higher dividend yields than most ordinary shares.
- Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs): According to Investopedia, Master Limited Partnerships are publically trader limited partnerships that usually focus on either realestate or natural resources sector. They often offer high income and different tax advantages than common stocks. These may pay a high dividend (called a distribution), but like all investments they are certainly not without risk.
- Utility Stocks: Utility stocks are known for their stable and predictable cash flows due to the nature of their business. Because they often have limited potential for growth through reinvestment of their corporate profits, they often have a higher dividend payout ratio and higher dividend yield than other stocks.
- Telecommunication Stocks: Similar to utilities, Telecommunication companies often pay high dividends due to their stable business models.
- Tobacco Stocks: Tobacco companies have also offered high dividend yields historically, although some ethical investors may not be willing to hold these stocks!
At this point I really want to emphasise that high dividend yields don’t come free… if a stock price is falling because their business is failing then the dividend yield will go up, however it is important to realise that dividend yields are backwards looking – the previous dividend divided by the current stock price. So if the market expects future dividends to drop then the stock price might fall resulting in a high yield, but if you purchased that stock you may never benefit from that yield if the company cuts its future dividends!
If you are doing fundamental analysis on a company then you may consider factors such as financial health, payout ratio, and dividend sustainability before investing in high-dividend stocks. If you are trading using technical analysis or systematically like I do, then you should consider the stock trend before investing. For example buying a stock with a high dividend yield that is above it’s 200 day moving average is less risky than a stock below it’s 200 day moving average because the stock above the 200 MA is trending up and so the share price is more likely to continue to go up over time.
If you want to find the stocks with the highest dividend yields now then you can use your stock screener (or this easy free screener from TradingView) to find stocks that meet your criteria. This screener will allow you to find the highest dividend stocks by yield and answer questions like ‘What is the highest paying dividend stocks?’.
If you are looking for the all-time best dividend stocks then conventional wisdom would suggest you look at the Dividend Aristocrat stocks which are stocks that have increased their dividend payment every year for the last 25 years.
Stock Dividend Aristocrats
Stock dividend aristocrats are an elite group of companies that have increased their dividends for at least 25 consecutive years. These companies are held up as the best of the best dividend paying stocks because of their financial stability and strength plus their focus on paying income to their investors.
These are absolutely solid performers when it comes to dividends, HOWEVER, investors should consider both capital gains and dividends before making a decision to invest. I have analysed the stock dividend aristocrats in more detail in this article and found no evidence to suggest that these stocks deserve your investment over any other stock in the S&P500 index!
The stock dividend aristocrat list seems to be a great marketing tool by the investment industry, but as is often the case it seems to be more fluff than substance as the total return from this group has not outperformed the S&P500 and a simple trend trading system applied to the S&P500 stocks outperforms the same system applied to the stock dividend aristocrats by a wide margin.
Dividend Yield: Is it a useful metric for evaluating stock dividends
Traders and investors may be tempted to look for stocks with the best dividend yield as one of their investment criteria. This is a simple and intuitively obvious way to find stocks to invest in, BUT does it give you an edge?
As always, my approach to answering questions like this is to develop a trading strategy and backtest it on historical stock data to determine how effectively the strategy worked. For the purposes of this investigation, I am going to test a variety of trading strategies that relate to dividends to determine if dividend yields are useful for evaluating stocks to buy.
There are three sections of this investigation:
- Dividend Yield Strategies
- Stock Dividend Growth Strategies
- Stocks with Monthly Dividend Strategies
Dividend Yield Trading Strategies
My goal in this section is to investigate whether the dividend yield provides useful information that can improve on buy and hold or simple trend trading that ignores dividend information. Here are the strategies we will evaluate:
- Baseline: Our baseline for comparison will be to buy and hold the SPY ETF which mirrors the S&P500 Index. We will use dividend adjusted data so it will give us the total return from our buy and hold investment.
- Trend Trading: We will use the same simple trend following system that I used to evaluate the stock dividend aristocrats that buys when a stock in the S&P500 makes a new 200 day highest close and holds until the stock closes below a 25% trailing stop. I will test several variations to determine the usefulness of dividend yields in our decision making:
- Model 1: Base model that ignores dividends and ranks trades based on 200 day Rate of Change
- Model 2: Only trade stocks that pay a dividend, rank trades based on 200 day ROC
- Model 3: Only trade stocks that pay a dividend, rank trades based on dividend yield
- Model 4: Only trade stocks with a high dividend yield (>2%), rank trades based on dividend yield
- Rotational Trading:
- Model 5: Each month, buy the 15 stocks from the S&P500 index that have the highest dividend yield and hold them until the following month. Then rerank all stocks, sell any holdings that have fallen out of the top 15 yielding stocks and buy new stocks that have entered the top 15 yielding stocks
- Model 6: Concentrated Rotational Trading. All rules as above but hold only 5 stocks instead of 15
Each of these trading strategies were backtested with Amibroker and Norgate data. The backtest results are shown below:

The highest performance out of all models presented was the simple trend trading system without any use of dividends. This gave the highest annual return and CAR/Max Drawdown (which is a measure of equity curve smoothness).
These backtests show that requiring a stock to pay a dividend, or ranking stock by dividend yield does not add any value over a simple trend following strategy. Similarly the rotational trading systems that actively select and hold the stocks with the highest dividend yields each month do not perform well compared to our simple trend following strategy.
As you can see, using the strategies listed above, there appears to be little benefit in using dividend yield as a filter or ranking factor.
Stock Dividend Growth – Does it predict stock price growth
Stock dividend growth is a measure of how much a company’s dividend payments have increased over time as measured by dollars per share. Companies with a history of strong dividend growth are demonstrating their ability to increase profits year on year and continue to increase the returns to shareholders. Dividend growth is generally considered by the market analysts as a sign of financial strength and stability because companies that can consistently increase their dividends are typically well-managed and have solid future prospects.
Investing in dividend growth stocks can provide investors with steadily rising income streams, as well as the potential for capital appreciation. As a technical trader I am interested in evaluating whether stock dividend growth is a good signal to trade a particular stock.
To evaluate whether stock dividend growth is a useful signal, I have compared Model 1 of our same simple trend trading system from above with a model that prioritizes trades in stocks that have the highest stock dividend growth. For these purposes I have adopted the following measure of stock dividend growth:
For the purposes of the backtest, I have used the Stock Dividend Growth as the Position Score. This means whenever there is more trading signals than available capital the signals are ranked from highest to lowest stock dividend growth and trades are taken from the top of the list first.
Here is the strategy:
- Model 7: Trend trading rules from Model 1 but rank positions on highest dividend growth using the above formula
The backtest for this trading strategy on the S&P500 stocks shows a meaningful improvement in performance compared to the Model 1 (The standard simple trend trading model without any reference to dividends. The compound annual return with this new stock dividend growth position score formula increased to 11.5% per year and drawdown reduced to 34% giving an uplift in CAR/Max Drawdown from 0.27 (for Model 1) to 0.34 (for Model 7).
This is a material improvement in system performance and is very interesting because it both improves return and reduces risk.
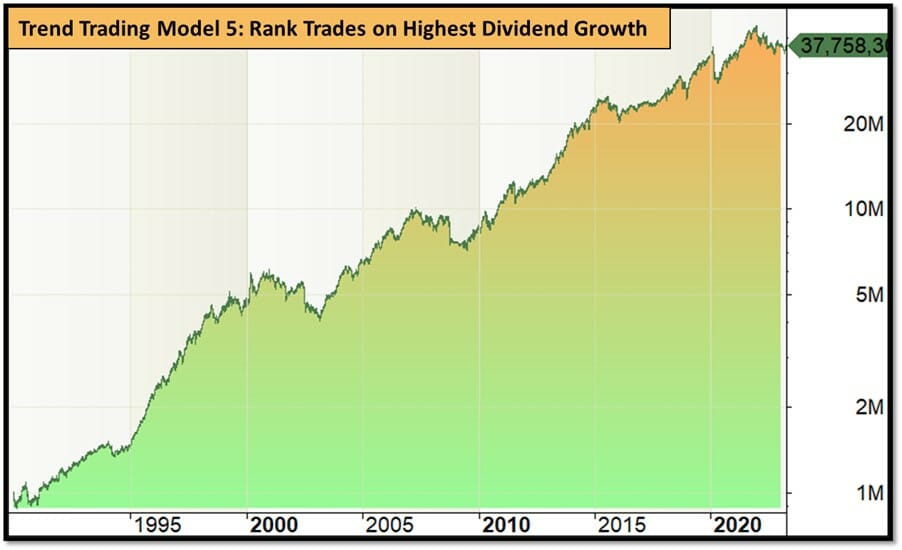
Now that we have seen how stock dividend growth improves a simple trend trading system, let’s test a rotational trading strategy that ranks all stocks in the S&P500 based on dividend growth using the same formula as the above and holds the top 15 dividend growth companies.
- Model 8: Each month, buy the 15 stocks from the S&P500 index that have the stock dividend growth and hold them until the following month. Then rerank all stocks, sell any holdings that have fallen out of the top 15 and buy new stocks that have entered the top 15 stock dividend growth.
Backtesting this rotational trading system from 1990 until 2023 we get the following results:

Um – Ouch. So clearly selecting stocks ONLY on the basis of highest dividend growth and remaining invested in them is a terribly losing strategy. As usual we find that simplistic rules (like these ones) don’t work, but elegantly simple rules (like Trend Trading with a dividend growth trade rank as in Model 7) do work.
Stocks With Monthly Dividends: A Unique Approach to Passive Income
Unlike most dividend-paying stocks that distribute payments on a quarterly or annual basis, stocks with monthly dividends provide shareholders with a more frequent income stream. These stocks are popular among income-oriented investors, such as retirees, who appreciate the regular cash flow for budgeting purposes or reinvestment opportunities.
As traders and investors it sounds like a good idea to hold stocks with monthly dividends, but as we have seen it is critical to backtest this idea and compare to a control group to see if this rule gives us a profitable edge rather than just a warm fuzzy feeling when we get a few bucks paid into our account each month.
We need to do a different test to evaluate whether stocks with monthly dividends are good investments because there are very few stocks with monthly dividends in the S&P500 Index. So for this test we adjust our simple trend following model to backtest all current and past stocks listed on the US main exchanges.
- Model 9: Buy when a stock makes a new 200 day highest close and the average daily turnover is above $1m. Hold until the stock closes below a 25% trailing stop. No reference to dividends (This is our new control)
- Model 10: Same as model 9, however it must be a stock with monthly dividends.
Model 9 gives us a compound annual return of 5.7% with a maximum drawdown of 56%. This is clearly not a tradeable strategy. When we add the requitement that the stock must pay monthly dividends the compound annual return falls to 4.4% which is not ideal, but the maximum drawdown fell by more than half to just 26%. While this is still not a tradeable strategy in my view, it does show that stocks with monthly dividends provide better risk adjusted returns.
As you can see from the two equity curves below, the equity curve for the stocks with monthly dividends is much smoother than the equity curve for all stocks.

This set of rules doesn’t excite me obviously, however it does show that there may be some benefit to adding a rule to your trading system requiring stocks with monthly dividends. This is something that I would recommend you test for each system you are trading and determine if it adds value on a system by system basis.
Conclusion on Stock Dividends
In conclusion, our investigation into various trading strategies involving stock dividends has shown that dividend yields and monthly dividend payments, on their own, may not necessarily provide a substantial edge for traders and investors. However, incorporating stock dividend growth as a ranking factor within a trend trading system demonstrated promising results, with improved returns and reduced risk.
Simplistic rules, such as focusing solely on high dividend yield or monthly dividend payments, may not yield the desired outcomes. Instead, more elegant trading strategies like trend trading combined with dividend growth ranking can lead to more meaningful trading edge. As with any trading strategy, it’s crucial to backtest and evaluate the effectiveness and stability of each system.
Ultimately, the key takeaway from this analysis is the importance of thorough testing and evaluation when developing trading strategies. Blindly investing using a dividend focused strategy without thoroughly backtesting it could result in very disappointing results.
The backtesting methodology, approach to coding, system templates and analysis used is all taught extensively in our flagship mentoring program, The Trader Success System.



