So you’re finally ready to start trading, and then the unexpected happens…
Your account blows up super quickly within the first few months, and you don’t understand why. One of the biggest causes of this early blow-up is an incorrect approach to position sizing methodologies and failing to manage your risk per trade technique effectively.
Proper position sizing techniques are a frequently neglected topic when learning trading strategies, yet they play a critical aspect of risk management in trading. If you don’t calculate the optimal position size, you may unknowingly take on considerable losses or expose yourself to volatile assets beyond your personal risk tolerance. This article will ensure that doesn’t happen to you!
By calculating position size consistently across all of your trades, you stabilize your account, maintain consistent risk exposures, and control your capital allocation per trade. This prevents a single asset’s potential risk from derailing your trading journey. In this video, I explain how to use adept position sizing techniques to stay consistent across all of your active positions.
What is Position Size in Trading?
Position Sizing The Right Way
Many ask if there’s a position sizing strategy or rule of thumb to follow. That’s why in this article, I’ll share how to calculate your calculated position size for any trades that you want to make—one of the most important lessons when you learn stock trading.
The first thing to look at before taking any trade is understanding the Risk per share or per contract. That way, you know on what basis to size your positions. For instance, let’s say you’re going to take a trade in this instrument, and this bar here is your entry bar. Identify that we get an entry signal right here at a share price of $3.48, for example.

How to Calculate Position Size in Stock Trading – Know the Risk Per Share
The first thing to do is set your stop-loss according to your trading strategies and system rules. That could be volatility-based sizing or basic stop loss principles. This stop-loss here is based on a certain multiple of the volatility of the average true range (there’s any number of ways you can do that).
We’ve got an entry price of $3.48 and an initial stop loss on this share of $3.25. That gives us a total loss distance of 23 cents. If you’re wrong on this single trade and we have one share, your money at risk will be 23 cents. Your job now is to figure out how many shares you should buy given this risk per trade of 23 cents and the size of your trading capital.
The Position Size Trading Formula
There are many position sizing techniques, but I’ll teach you the basic formula you need to know to make sensible choices.
Here’s how to calculate position size in trading using a simple formula:
The number of units that you buy = (equity in your account × risk per trade) / risk per unit.
Position Sizing Formula for Stock Trades (Percent Risk Model)
- Equity is the total amount of money in your account.
Multiplied by percentage risk per trade, you might be risking 1-2% to risk of your account on each stock trade. If you’re wrong, you’ll lose 1% stop-loss of your investment capital on this trade. Divide that by the loss price per unit (calculated on the previous slide) to determine how many total units you can buy.
This ensures that all trade sizes are adjusted so that the positions give the same dollar risk per trade across different financial instruments.
What you want to avoid as a trader is inconsistency, such as having a $500 loss percentage on one trade, a $3,000 loss level on another, a $10,000 book loss on another, and a $2,000 consecutive loss on another because you’ve got random position sizes all over the place.
One of the first steps toward a consistent risk management approach when you learn stock trading is standardizing your allocation per trade so that if you’re wrong, you’ll lose the same acceptable level on each trade.
You get much greater consistent success and a sense of confidence in market predictions because you know how much you’ll lose when you’re wrong and how much that’ll impact your capital to risk. You can then start to manage your risk in trading more successfully.
It also gives your trades the same profit target potential. If you size your trades based on a volatility stop-loss, each has an equal chance of success or failure.
For instance, if you buy a $50,000 position in a volatile asset like Facebook and a $2,000 position in a single asset like Apple, then the larger position size in Facebook is going to have a much higher relationship between risk and reward and higher potential returns than the Apple position. With the Position Size limit formula, you can standardize your trades’ profit and loss potential.
Let’s take an example using the same chart we discussed. Suppose you have $10,000 of investment capital and want to risk 1% per trade. How does that calculation work?


Position Sizing Formula Example to Help You Learn Stock Trading Safely
Let’s break this down with an example:
- You have $10,000 trading capital
- You decide on a 1% risk per trade, meaning you’ll risk $100 per trade
- Your risk per unit (stop-loss distance) is 23 cents per share
Number of shares to buy = ($10,000 × 1%) / $0.23
= 434 shares
If you take this single position and your initial stop-loss is hit, you’ll only lose $100 (1% of your trading capital).
What’s the value of that position?
To calculate the total position value, multiply the share price by the number of shares:
$3.48 × 434 shares = $1,510
This means you are taking on a $1,510 position while keeping your maximum risk limited to $100 in your $10,000 account.
Why would you do this?
Using proper position sizing allows you to risk a small portion of your capital at risk on each trade. This gives you a buffer so you can be wrong multiple times without suffering excessive losses.
For instance, if you risk less than 1% per trade, even a series of losing trades won’t destroy your account. Remember, in the early stages of stock trading, avoiding significant losses is just as important—if not more—than achieving potential gains.
Why Conservative Position Sizing Keeps You In The Game
Many traders make the mistake of risking too much per trade, thinking that bigger bets lead to bigger profits. But in reality, conservative position sizing is the key to staying in the game and avoiding catastrophic losses.
The Danger of Risking Too Much
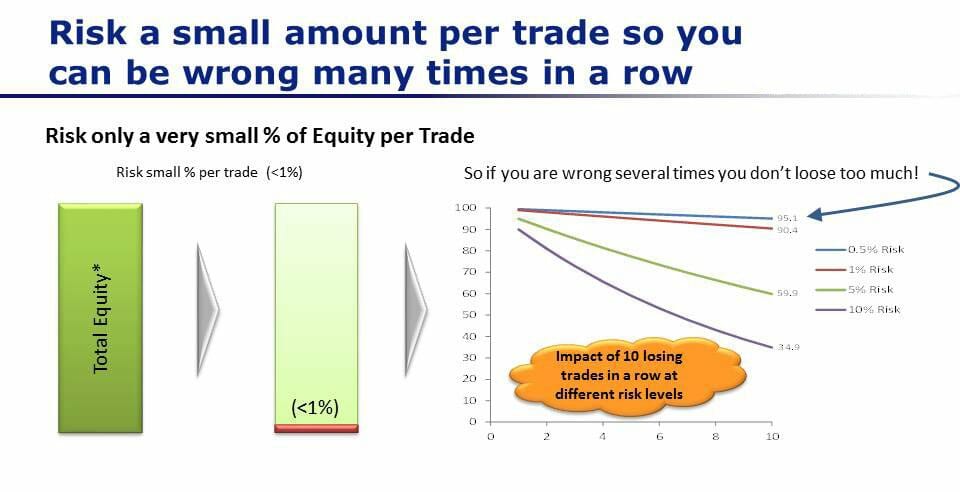
Let’s compare different risk levels and their impact on your trading capital after 10 consecutive losing trades:
- 10% risk per trade → Your account drops from $100 to just $34
- 5% risk per trade → Your account shrinks to $59
- 1% risk per trade → You still have $90 left
- 0.5% risk per trade → You’re down only $95
The takeaway? The smaller your risk per trade, the longer you can survive losing streaks without blowing up your account.
Why position sizing should be conservative when you learn stock trading
If you’re wrong only one time and you risked 10% of your trading capital, then you’re already down to 90% of the original. By the time you take 10 losing trades in a row (risking 10% per trade), you’re down to $34 from your starting point of $100.
Based on that, risking 10% of your capital on each trade is way too much.
If we risk 5% risk per trade, then you’re down to about $59 at the end of 10 losing trades.
If you risk only 1% risk per trade, you’re down to $90. If you risk only 0.5% risk per trade, then after 10 trades you’re down to only $95.
So what you can see is that the lower risk percentage per trade, the more potential losses you can sustain without blowing up your account.
So what you can see is that the smaller amount you risk per trade, the more losing trades you can have in a row without badly damaging your account. I would certainly advocate for most people to consider risking less than what you already are. If you’re risking in the vicinity of 5 or 10%, chances are you’re risking way too much money on each trade.
Take a good look at how many losing trades you can potentially get in a row and consider reducing your risk so that you’re not damaging your account if you get a string of losing trades.
You might think, “10 losing trades in a row, who would be so stupid as to lose that much money?” If you’re a trend follower, then you’ll probably make your money on a small number of trades, and have a large number of small losing trades.
Let’s say you try the trend following system like I do, you might be right 30% of the time and wrong 70% of the time. That sounds pretty bad, except when you realize that when I’m wrong, maybe I lose $1,000. But when I’m right, I make $10,000.
When the size of the losses is a lot smaller compared to the size of the gains, you can actually afford to have quite a low reliability or a lot of losing trades.
If you’ve got only 30% winning trades and 70% losing trades, you can actually get a very long losing streak. That’s why I highly suggest that you risk a small percentage of your account on each trade.
Using correct position sizing techniques is critical to effective risk management and long-term trading success. Whether you trade stocks, forex, or commodities, applying adaptive position sizing strategies will help protect your trading capital and keep you in the game for the long haul.
Position Size Small To Avoid Big Drawdowns
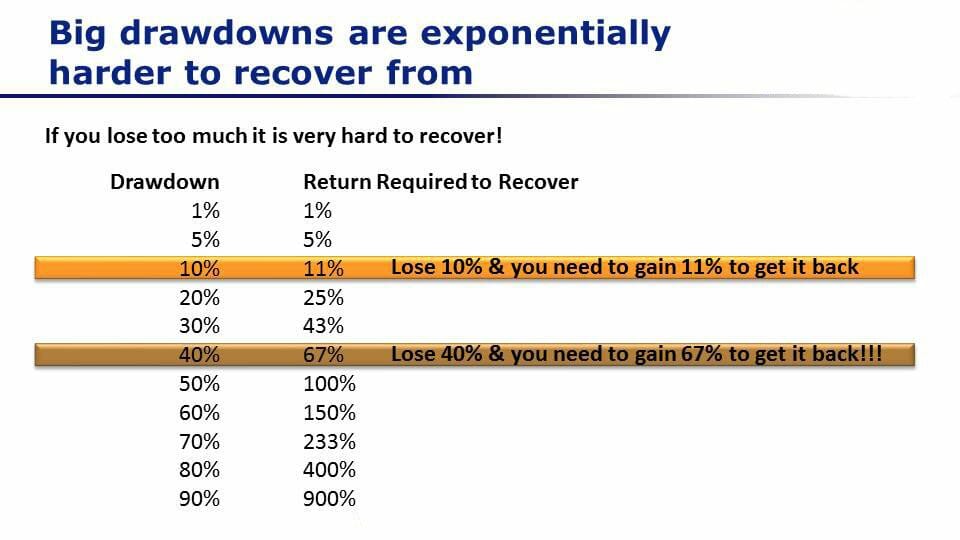
Drawdowns are inevitable in trading, but big drawdowns can cripple your ability to recover. The key to long-term success is keeping your losses small so you don’t have to fight an uphill battle just to get back to where you started. What if you get a big loss or a drawdown in your trading account? Check out this example in the photo. You’ll first see a level of drawdown and then in the next column how much return on investment (ROI) you have to make in order to recover your initial account size.
Big drawdowns are particularly scary when you’re learning stock trading, so this is something you’ll want to understand!
Be careful of big drawdowns while you learn stock trading
Let’s say you have a drawdown, you lose 10% of your account so you started at $10,000, you lose 10%; You’re now down to $9,000. In order to get back to your initial $10,000, you need to make 11% because of the asymmetry of returns. Losing 10% means you have to make 11% back. That’s pretty similar so that’s not such a big deal, but when you start to get bigger and bigger drawdowns, this becomes more and more of a problem.
Say you get a drawdown of 40%. You start at $10,000 and your account drops to $6,000. In order to get back to your original $10,000, you now need to make a 67% return. That becomes a huge challenge to break even and then going on to make a profit.
If you lose half your account (from $10,000 down to $5,000) you then need to double your money from $5,000 back up to $10,000. That means you need to get a 100% return just to break even.
You can see that the biggest challenge or the biggest driver of success in trading is going to be limiting your drawdown so that when you go on to make more money, you don’t have to make excessively higher returns to get back to where you started.
You should always be aiming to keep your drawdown in a low range because that way you can very easily go on to make new account highs. If you’re having big drawdowns like 40 to 70% or more, then it’s almost impossible to get back to where you started.
That makes it very difficult to make money trading in the long run.
Trading System Risk Management And Position Sizing To Avoid Blowup
When you learn stock trading, it is so easy to underestimate the risk management you are taking on in each and every trade – I mean, after all, you are using stop losses…
(Seriously though, you are using stop losses, aren’t you?)
The trouble is that sometimes something unexpected happens and stop losses can’t always save you.
Like the time earlier this year when a position I was in dropped 47% overnight and was immediately suspended from trading. I have no idea how much I will lose on the trade, but it doesn’t matter because I followed the trading strategy I am giving you in the video below.
In this video, I explain why risk management is so important and why you should risk only a very small percentage of your trading account on each trade. I hope you enjoy it!
What About The Dangers Of Risking Too Much On A Single Stock Trade?
This is particularly important when you’re learning stock trading using a system as a long-term trend following system with a large number of small losing trades to a small number of large winners.
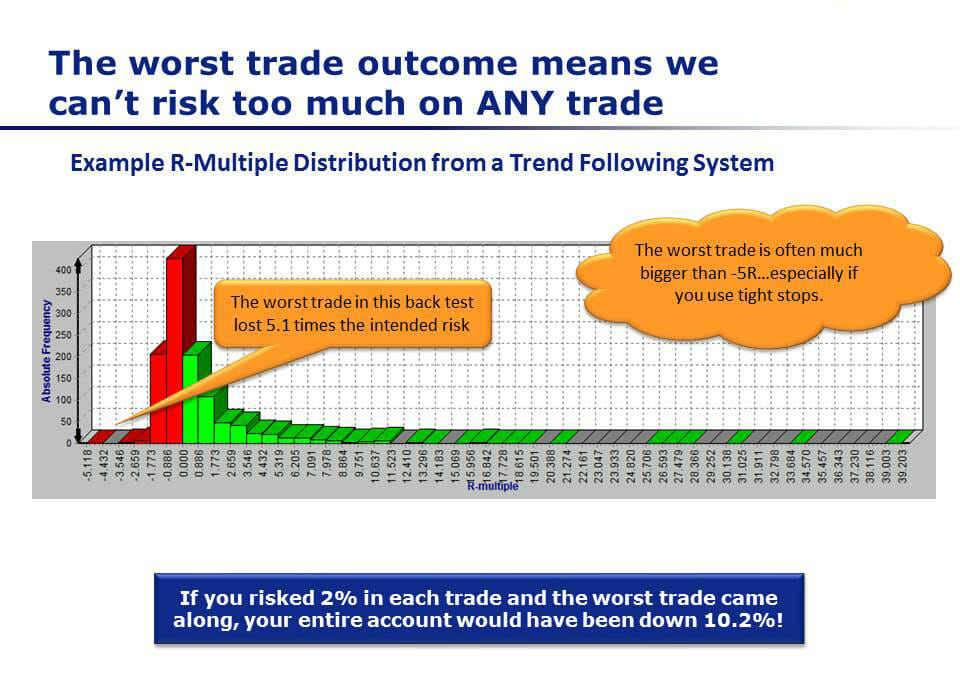
In this photo you’ll see the trade distribution profile of a typical trend following system. The particular details of the system don’t matter, but basically in any trend following system that you use (any system that cuts losses short and lets profits run) you’re going to get a profile of trades like this one.
The worst trade outcome means we can’t risk too much on ANY trade.
Learn stock trading – risk management by conservative position sizing
You’ll see on the right-hand side a small number of very large winners. This is where the bulk of your profits come from.
Then, you have a larger number of small winners. These are the ones that really help you break even.
Then, you’ve got a large number of small losses. These are the things that chip away at your account. And this is where you’re going to manage your risk day today.
Now, the key thing that you can notice if you look carefully here on the very left-hand side is the worst single trade in this entire backtest, a loss of 5.1 multiplied by the intended risk.
What this chart represents is the number of trades on the left-hand column, and the R-multiple.
If you intended to risk $1,000 dollars, and you won $2,000, then your R-multiple is 2.
If you intended to risk $1,000, and you lost $1,000, then the R-multiple would be -1.
This losing trade over here on the very left-hand side lost 5.1 multiplied by the maximum intended risk. Now, that’s one trade out of probably thousands on this chart. If that one trade existed in the backtest, then chances are that one trade, or worse, could also exist in the future in your system.
Now, when you’re managing your risk for a trading system, make sure that your system will survive and that you can profit regardless of what the market throws at you in the future.
The fact is, a -5 R-multiple trade that existed in the past could come back and bite you in the future. Make sure that the risk-per-trade you take on takes into account the worst trade in your backtest. Ensuring that your account survives the worst expected trade (and then some) is an important step to take early as you learn stock trading.
As an example: if you risked 2% on each trade that you took using this system and that trade came along this 5R loss, then your entire account would have been down by 10.2% just because of that one trade.
Now I don’t know about you, but I want to make sure that my account isn’t so sensitive or volatile to any one trade outcome. A single trade losing 10.2% (especially when I know that trade is there in the backtest and therefore potentially might come along again in the future) is simply an unacceptable risk.
Why The 2% Position Size Rule Is Garbage
(2% Is Way Too Much Risk!)
When you look at your trade distribution profile like this in terms of R-multiples, you need to make sure that you’re comfortable with the amount that you’re risking and what that’ll translate to in terms of the worst possible loss.
This is why I teach people that (when doing trend following trading) to risk much less than 2% per trade.
A lot of authors and educators out there talk about the 2% rule and the reason people talk about risking no more than 2% is not that it’s the right amount across the board for everyone. It’s actually because if an educator talks to someone and says, “You should risk .2% of your account on each trade,” most people will be like, “You’re on drugs because how can you possibly make any money risking so little?”
The reality is that most people don’t have a clue how to make good consistent profits in the market.
And most people don’t understand how to stop themselves from blowing up when the market turns against them. 2% is a very rough and actually quite aggressive guidance for stop people from doing really crazy things like risking 5 or 10% of their account on each trade.
The other thing to keep in mind, though, is that while this trading system example generated a -5 R-multiple loss, the worst-case trade is often far bigger than the -5R that we see here. I’ve seen trading systems (some that I’ve tested and played with) where the worst-case loss was -10, -20. You don’t get very many of those, but you’ve got to be very careful with how you position size, in case those sorts of things come along.
What Causes Big R-Multiple Losses?
What drives the very big R-multiple losses in many cases is a really tight stop-loss. If you’re using a tight stop-loss and you get a gap down or a gap against your position, you run the risk of getting big R-multiple losses.
As my accounts grow and as I’ve adjusted my risk profile to be a little more conservative, I started to use slightly wider stop losses and also smaller and smaller position sizing for each trade. That’s enabled me to have the confidence that I’m not going to lose big money when a bad trade comes along.
I hope that’s been useful and I look forward to seeing your questions and comments in the video stream below.
What are the best position sizing models?
Choosing the right position sizing model is crucial for managing risk and maximizing returns in both stock and crypto trading. Let’s break down the most effective models and when to use each one.
But before we dive in, here’s a key takeaway: Never assume the default position sizing method in a trading system is the best for you. Every trader has different goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions to consider.
When you’re doing position sizing, there’s a couple of different general models:
- Percent of Equity Position Sizing
- Percent Risk Position Sizing
- Volatility Based Position Sizing
Try our Position Size Calculator
Our Position Size Calculator can do the heavy lifting for you for each of these three position sizing models. Click here to try it out today!
There are three major position sizing models:
Percent of Equity Position Sizing Model
This method allocates each trade a fixed percentage of your total account balance.
Example:
- You have a $100,000 account and decide to use 5% of equity per trade.
- Each trade will have a position size of $5,000 (5% of $100,000).
- If the stock price is $50 per share, you buy 100 shares.
Pros: Simple and easy to apply.
Cons: Does not account for different risk levels between trades.
Percent Risk Position Sizing Model
This method normalizes risk per trade by adjusting position size based on the difference between your entry price and stop-loss.
Example:
- You risk 1% of your account per trade (on a $100,000 account, that’s $1,000).
- You plan to enter a stock at $20 per share with a stop-loss at $18 (a $2 per share risk).
- Your position size is $1,000 ÷ $2 = 500 shares.
Pros: Controls risk consistently across different trades.
Cons: If your stop-loss is too tight, small price fluctuations can stop you out too often.
Key Insight: Many traders think a 1% risk is “too small,” but the truth is that risking more than 1% can wipe you out quickly. A few big losing trades—especially if the market gaps against you—can cause massive drawdowns if you’re risking too much per trade.
Volatility-Based Position Sizing Model
This model adjusts position size based on market volatility to ensure each trade has a similar dollar fluctuation in your account.
Example:
- You want each position’s volatility to be 0.5% of your account.
- You have $100,000 and the stock’s ATR (Average True Range) is $1.50.
- Your target fluctuation is $100,000 × 0.5% = $500.
- Your position size is $500 ÷ $1.50 = 333 shares.
Pros: It helps smooth out fluctuations across different trades, and it is especially useful when no stop-loss is used.
Cons: Requires careful backtesting to determine the right volatility percentage for your system.
Which Position Sizing Model Is Best for You?
It depends on your system and risk tolerance:
- Beginner traders → Percent of Equity (simple and easy to implement).
- Trend followers and breakout traders → Percent Risk (ensures consistent risk per trade).
- Traders without stop-losses or in volatile markets → Volatility-Based (normalizes trade fluctuations).
So when exactly should you use each position sizing model?
Use percent of equity position sizing is best when there’s a high risk of a catastrophic move against you, hurting you in a single stock, particularly with short positions or with tight stop-losses.
Use percent risk position sizing on the long side when you have a fairly wide stop loss in a trend following system.
Use percent volatility position sizing as a backup when you don’t have a stop-loss, but I want to normalize the dollar fluctuations across your trades.
There is a hybrid option, which is nice when combining the percent risk and the percent equity. So you can position size, half a percent risk per trade, but cap exposure on any one stock at 10% or 5%. This is a useful approach because sometimes with a percent-risk model (particularly if you’ve got a stop-loss which is volatility linked) your risk-based position sizing will give you a huge position size. This presents an unacceptable stock-specific catastrophic risk, so you also add a percent of equity cap of 5% to control this risk.
For example: if you have a $100,000 account and you’re risking 0.5% of equity per trade. Your entry price is $20 and the stock has traded in a tight range recently so the ATR-based stop loss is only $0.50/share wide. The risk-based position size model would tell you to buy how many shares? $100,000 x 0.5% / $0.50 = 1,000 shares = $20,000 exposure on this $20 stock… That is TOO MUCH EXPOSURE!!!
So if you also add the 5% of equity cap, your position size would be capped at $5,000 (250 shares) on this trade, so the catastrophic stock risk is much reduced compared to risk-based position size alone.
If you combine the risk-based position sizing model and the percent of equity position sizing model like this you get the best of both worlds. Your percent risk model gives you your day-to-day general returns and drawdown profile you’re comfortable with. However, the percent of equity cap limits your catastrophic risk to a level that you’re comfortable with.
You may or may not see the benefit of that in the backtest, but you do want to think about your risk management beyond what you see in the backtest, which is why the percent of equity cap is useful.
Which position sizing model should you start with?
If you’re building a trading system, start with the 5% of equity position sizing model and then experiment with the others. The best approach is to test all three models (Percent of Equity, Percent Risk, and Volatility-Based) to see which one works best for your strategy.
Why? Different systems perform better with different position sizing models. That’s why I don’t use the same one for every system. Each model is fine-tuned through backtesting and optimization (I do this using Amibroker).
Keeping It Simple
If you want an easy starting point, using a single position sizing model across your whole portfolio is an option.
For example:
- A Percent of Equity model would ensure thatno single trade wipes you out.
- This approach can work if it blends well with the other systems in your portfolio.
But here’s the key:
Position sizing should be tailored to each trading system first. Then, once you have multiple systems, you can optimize position sizing across the entire portfolio.
If you’d like to learn how to trade systematically and build a diversified portfolio of trading systems (including portfolio position sizing) that incorporate all of the risk management and position sizing considerations discussed in this article, then you should join The Trader Success System today and experience an acceleration towards your trading goals!
Frequently Asked Questions about Position Sizing
What is the position sizing method?
Position sizing is a crucial aspect of trading that determines how much capital you allocate to each trade. It’s all about managing risk and ensuring that no single trade can significantly impact your overall portfolio. Here’s a quick rundown of some common position sizing methods:
- Percent of Equity: Allocate a fixed percentage of your total equity to each trade. This method keeps your exposure consistent across trades .
- Risk-Based Position Sizing: Determine position size based on the amount of risk you’re willing to take on each trade. This involves calculating the difference between your entry price and stop loss, ensuring that your potential loss is a fixed percentage of your account .
- Volatility-Based Position Sizing: Adjust position size according to the volatility of the asset. More volatile stocks get smaller positions, while less volatile ones get larger positions, aiming to normalize risk across trades .
These methods help traders maintain consistency and manage risk effectively. If you’re looking to dive deeper into position sizing, Van Tharp’s “The Definitive Guide to Position Sizing” is a fantastic resource that I highly recommend . It covers various models and their advantages and disadvantages, helping you tailor your approach to meet your trading objectives.
How do you calculate position size?
Calculating position size is a fundamental part of managing risk in trading. Here’s a straightforward way to do it:
- Determine Risk Per Share: Start by setting your stop-loss according to your trading system rules. This could be based on volatility or chart patterns. For example, if your entry price is $3.48 and your stop-loss is $3.25, your risk per share is $0.23 .
- Decide on Risk Per Trade: Decide what percentage of your total account you’re willing to risk on each trade. A common approach is to risk 1% of your account per trade. So, if you have a $10,000 account, you’d risk $100 per trade .
- Calculate Position Size: Use the formula: [ \text{Position Size} = \frac{\text{Account Equity} \times \text{Risk Per Trade}}{\text{Risk Per Share}} ] For example, with $10,000 equity, 1% risk per trade, and $0.23 risk per share, you’d calculate: [ \text{Position Size} = \frac{10,000 \times 0.01}{0.23} = 434 \text{ shares} ] This ensures that if your stop-loss is hit, you only lose $100 .
By standardizing your position size, you maintain consistent risk across trades, which is crucial for long-term success.
What is the best position sizing strategy?
The best position sizing strategy really depends on your trading goals and risk tolerance. Here are a couple of strategies that I often recommend:
- Risk-Based Position Sizing: This is my preferred method. It involves calculating the risk per share (the difference between your entry price and stop-loss) and ensuring that your potential loss on any trade is a fixed percentage of your account. For example, if you have a $100,000 account and want to risk 1% per trade, you’d risk $1,000. You’d adjust the number of shares you buy so that if your stop-loss is hit, you only lose that $1,000 .
- Volatility-Based Position Sizing: This method adjusts your position size based on the stock’s volatility. You’d buy fewer shares of more volatile stocks and more shares of less volatile ones. This way, the day-to-day fluctuations in your portfolio are more consistent in dollar terms. It uses the Average True Range (ATR) to determine volatility and adjusts the position size accordingly .
Both methods aim to normalize risk across trades, but they do so in slightly different ways. Risk-based sizing focuses on potential loss, while volatility-based sizing focuses on price movement. It’s crucial to backtest these strategies to see which aligns best with your trading style and objectives .
What is the 2% rule in swing trading?
The 2% rule in swing trading is a risk management guideline suggesting that you should never risk more than 2% of your account on a single trade. The idea is to protect your capital from significant losses, allowing you to survive through losing streaks. However, it’s important to note that this rule can be quite aggressive for many traders.
- Volatility: Risking 2% can lead to volatile results, especially if your stop-losses aren’t executed perfectly. A sudden drop or unexpected event can significantly impact your account .
- Conservative Approach: Many experienced traders, including myself, recommend risking much less than 2% per trade. Personally, I risk about 0.5% or even less. This approach allows you to endure multiple losses without a devastating impact on your account .
- Survival: The key is to ensure that no single trade outcome can take you out of the game. By risking a small amount, you can withstand a series of losses and still have the opportunity to recover when your system aligns with the market again .
Ultimately, the right risk level depends on your trading system and personal risk tolerance. It’s crucial to backtest your strategies to determine what works best for you.
How can a beginner learn about position sizing?
Learning about position sizing is crucial for any beginner in trading. It’s all about managing risk effectively to ensure long-term success. Here’s a simple way to get started:
- Understand the Basics: Begin by familiarizing yourself with the concept of risk management. Position sizing is a key part of this, as it determines how much of your capital you allocate to each trade .
- Learn the Methods: There are several position sizing methods, but the most common ones are:
- Percent of Equity: Allocate a fixed percentage of your total equity to each trade .
- Risk-Based Position Sizing: Determine position size based on the amount of risk you’re willing to take on each trade .
- Volatility-Based Position Sizing: Adjust position size according to the volatility of the asset .
- Use Tools: Consider using a position size calculator to simplify the process. This tool can help you quickly determine the appropriate position size based on your chosen method .
- Start Small: As a beginner, it’s wise to start with small position sizes to protect your capital while you learn and gain experience .
- Practice and Backtest: Use historical data to backtest your position sizing strategy. This will help you understand how it performs under different market conditions .
By focusing on these steps, you’ll build a solid foundation in position sizing, which is essential for effective risk management in trading.
What is an example of position size?
Let’s walk through an example of calculating position size using a risk-based approach, which is a method I often recommend. Suppose you have a $20,000 trading account and want to risk 1% of your account on each trade. Here’s how you’d calculate it:
- Determine Risk Per Trade: With a $20,000 account, risking 1% means you’re willing to lose $200 on a trade .
- Calculate Risk Per Share: Let’s say you’re buying a stock at $15 per share, and your stop-loss is set 10% below your entry price. That means your stop-loss is at $13.50, giving you a risk of $1.50 per share .
- Calculate Position Size: Use the formula: [ \text{Position Size} = \frac{\text{Risk Per Trade}}{\text{Risk Per Share}} ] So, you’d calculate: [ \text{Position Size} = \frac{200}{1.50} = 133 \text{ shares} ] This means you can buy 133 shares, and if your stop-loss is hit, you’ll lose $200, which is 1% of your account .
This approach ensures that your risk is consistent across trades, which is crucial for long-term success.
Why is position sizing important?
Position sizing is absolutely crucial in trading because it directly impacts your risk management and long-term success. Here’s why it matters:
- Risk Management: Position sizing helps you control how much of your account you risk on each trade. By standardizing your risk, you avoid large, unexpected losses that can wipe out your account .
- Consistency: Using a consistent position size ensures that your losses are predictable and manageable. This consistency is key to building confidence and maintaining discipline in your trading strategy .
- Staying in the Game: The primary goal in trading is to stay in the game long enough to capitalize on profitable opportunities. Conservative position sizing helps you survive losing streaks and avoid catastrophic drawdowns .
- Psychological Comfort: Smaller position sizes reduce stress and emotional decision-making. When your risk is controlled, you can focus on executing your strategy without the fear of significant losses .
- Avoiding Overconfidence: By treating all trades with the same level of risk, you avoid the temptation to “load up” on trades you think are sure winners, which can lead to significant losses if you’re wrong .
Ultimately, position sizing is about protecting your capital and ensuring that you can trade another day, which is far more important than any single trade’s outcome.
Can position size guarantee profit?
Position size, while crucial for risk management, cannot guarantee profit. Here’s why:
- Risk Management, Not Profit: Position sizing is about managing how much you risk on each trade, not about ensuring profits. It helps protect your capital by limiting losses, but it doesn’t influence whether a trade will be profitable .
- Consistency Over Time: By maintaining a consistent position size, you give each trade an equal chance to succeed, which is important for realizing the long-term profitability of your trading system. However, this doesn’t mean every trade will be a winner .
- Market Unpredictability: The market is inherently unpredictable, and no amount of position sizing can change that. You can’t know in advance which trades will be successful, so treating all trades with the same risk level is key .
- System Edge: Profitability comes from having an edge in your trading system, not from position sizing alone. Position sizing helps you survive the inevitable losing streaks and capitalize on your edge over time .
In essence, position sizing is a tool for risk management, ensuring you can stay in the game long enough to let your trading edge play out.
Why do we use a specific formula for position sizing?
Using a specific formula for position sizing is essential for several reasons, all tied to effective risk management and consistent trading performance:
- Standardization: A formula ensures that your position sizes are consistent across trades, which is crucial for maintaining a predictable level of risk. This consistency helps avoid large, unexpected losses that can occur if position sizes vary widely .
- Risk Management: By calculating position size based on your account equity and risk per trade, you can control how much of your account is at risk on any given trade. This approach helps protect your capital and ensures that no single trade can cause significant damage to your account .
- Confidence and Discipline: Knowing exactly how much you’re risking on each trade gives you confidence and helps maintain discipline. When you have a clear plan, you’re less likely to make impulsive decisions based on emotions .
- Long-term Success: Consistent position sizing allows you to survive losing streaks and capitalize on winning trades, which is essential for long-term profitability. It ensures that your trading system’s edge can play out over time without being derailed by a few bad trades .
- Adaptability: Different position sizing models, like percent of equity or percent risk, allow you to tailor your approach based on your trading style and market conditions, providing flexibility while maintaining control over risk .
Using a formula is about ensuring that your trading remains systematic and that your risk is managed effectively, which are key components of successful trading.
What is the formula to calculate position?
The formula for calculating position size in trading is crucial for managing risk effectively. Here’s how you do it:
- Determine Risk Per Share: First, set your stop-loss according to your trading system rules. For example, if your entry price is $3.48 and your stop-loss is $3.25, your risk per share is $0.23 .
- Decide on Risk Per Trade: Choose a percentage of your total account you’re willing to risk on each trade. A common approach is to risk 1% of your account per trade. So, if you have a $10,000 account, you’d risk $100 per trade .
- Calculate Position Size: Use the formula: [ \text{Position Size} = \frac{\text{Account Equity} \times \text{Risk Per Trade}}{\text{Risk Per Share}} ] For example, with $10,000 equity, 1% risk per trade, and $0.23 risk per share, you’d calculate: [ \text{Position Size} = \frac{10,000 \times 0.01}{0.23} = 434 \text{ shares} ] This ensures that if your stop-loss is hit, you only lose $100 .
By standardizing your position size, you maintain consistent risk across trades, which is crucial for long-term success.
Links to Articles About Position Sizing
Explore more insights into position sizing and improve your trading consistency! Visit our detailed article on how to calculate position sizing for all the details.
- How To Calculate Position Sizing | What Is The Best Way?
- Profile of Van Tharp
- The Dangers of Martingale Position Sizing in Trading
- Position Sizing In Amibroker With SetPositionSize Function
- Master Risk Management for Traders: Proven Strategies to Protect Your Capital and Maximize Profits
- How to become a consistent trader?
- How can I overcome my fear of taking action when trading stocks?
- Trading Psychology | 4 Causes of trading stress and anxiety PLUS how to eliminate them
- Van Tharp – Outstanding Trading Books And Resources To Improve Your Performance
- 4 things you must do to survive stock market volatility
- Is it possible to mitigate huge potential losses?
- Kelly Criterion: The Smartest Way to Manage Risk & Maximize Profits




Hello Adrian.
A lot of very useful information for people in your article.
There is one aspect that in nearly every article I have read both online and in books doesn’t cover.
The ‘equity’ level that is used to calculate the PS.
There are 2 schools of thought on this.
To calculate equity you can use cash levels plus the value of open positions. I used to do it this way, it is more aggressive you could say.
Your equity value varies with the mark to market price at the end of each day for your portfolio.
The other way is to use the cash level plus the purchase cost of the positions in the portfolio.
This way the equity remains constant except when a position is closed. It doesn’t vary with the portfolio closing price each day.
I use the latter now as I realised that if your portfolio has a large amount of unrealised profits you can end up taking larger positions that can be riskier especially if the market has had a good run for a while.
I’d be interested to hear your perspective.
It is a little harder to test than the open equity model.
Hi Neil,
Great question – thank you for taking the time to ask. There are several approaches to this, however I use what is probably the simplest – Total Equity. For each new trade I look at the total liquidation value of my account and use that level for position sizing. The advantage of this is that the growth in account caused by long term trend following trades that can remain open for months benefits the shorter term systems with increased size while the trend following positions are still open. Probably the most important factor here is that it is critical to “test what you trade and trade what you test”… Amibroker uses total equity when backtesting, so that is what I do in my live trading also. The level of ‘aggressiveness’ of this approach is higher than using what some call ‘closed trade equity’, but I make up for that by using more conservative position sizing and lower leverage levels than most traders.
There are advantages and disadvantages either way, but I would say simple is best and make sure you are trading what you test.
Adrian
One question: what would the formula look like if I had to incorporate the price charged by the exchange into the size of the position? sometimes my stop loss point is very close to the price and I have a position size whose exchange rate is already higher than my account’s maximum 1% loss limit.
Hi Gerard,
If your stop loss is that close to price and you are risking 1% of your account there is a significant risk of a position gapping through your stop and causing you a very large loss that could threaten the survival of your account. From what I have seen stop losses that tight lead to a high percentage of losing trades and with many strategies you can actually make more money by widening your stop and taking smaller (and therefore less risky) positions. If you want to include the commission in your position size, the simplest way to do it is to subtract the commission percentage from your target risk per trade. So if your commission & slippage assumption is 0.25% per trade and you wanted to risk 1% of your account per trade (including slippage and commission) then you would introduce a new parameter to calculate position size something like this:
AccountSize = 100000;
TotalRiskPerTrade = 0.01;
SlippageandCommission = 0.0025; // 0.25% per side
PositionRiskPerTrade = TotalRiskPerTrade – 2 * SlippageandCommission; // Slippage and commission multiplied by 2 because you have to Buy and Sell
RiskPerShare = (EntryPrice – StopPrice);
NumberofShares = (AccountSize * PositionRiskPerTrade ) / RiskPerShare ;
In this example you would therefore only risk 0.5% per trade
Where to set initial Stop Loss? can your back testing show an optimum place for stop loss and what is suitable distance for trailing stop? can back test find these?
Hi Baz,
Great question – Yes absolutely stop loss width is a ‘rule’ in your system like any other and you can very the value for the width of the initial stop loss to find the best values for the system. Your stop loss might be a percentage based stop, in which case you can start at say 5% and increase it to 50% in steps of 5% to see how the system performs as you widen the stop. If you have an ATR based stop, you might start at 1xATR for example and increase it to 8xATR in steps of 0.5xATR and see where the best performance is. This is very easy when you are doing systemised backtesting… super powerful stuff.
Thanks Adrian, a great piece. To a degree I think you need to tailor position sizing to your personality, albeit with the caveat that there is great danger in having too high position sizing.
I typically am quite conservative, and often when starting out a new system to get a feel for it will start with a much lower size and then increase gradually as I get more comfortable. One technique I use with my mean reversion day trade was to start at a fixed amount, say even as low as 1k for trade size(using fixed % stop loss), and then each month if I have made a profit to increase the size. If I have made a loss then wait till I make up for that loss before increasing the size again. This suits me and makes trading a new system less ‘scary’.
Great insights – thank you for sharing Tim. I do like the scaling up a new system idea if you find it uncomfortable to start at full size. You are 100% right the position sizing needing to match your personality and objectives – this is very important. If you have a lower drawdown tolerance then a lower position size will usually be the right answer.
Hi Adrian,
How can I take advantage of favorable market conditions? There are times when my trading system is very aligned with the market. Metrics such as consecutive winners, PnL, MFE, are doing very good for several trades in a row. There are also times that my system is just not aligned with the markets, and the opposite happens, I have several trades in a row that are losers, even though I consistently follow my trading system. How can I adjust my position size, so that when I know that my system is aligned with the markets I increase my risk exposure, but when the opposite happens, I reduce exposure? Does that make sense? I currently use a Percent Risk Position Sizing. Thanks!
Hi Rodrigo,
Great question! I would start by generating some hypotheses about when your system is in sync with the market and when it is not – let’s say when the index is trending up and the volatility of the index is low your system performs best (for example in pseudo-code: InSyncConditions = Index > EMA(Index,200) and IndexATR(14)/Index < X%) Then in your system code you would create a rule that says IF InSyncConditions is true, then set risk per trade to 2%, else set risk per trade to 1%. Then backtest the system with this rule and compare it to a constant 1 or 2% risk per trade.
Great to clarify the various types of stops .
With relatively small total equities say $5 or 10K parcel size could be an issue on ASX . thoughts…? save a little more
Hi Adrian. A very informative article. I’ve only recently toyed with the idea of using the ATR as a stop loss, and have been concerned about how to calculate my risk, and therefore position size. Now I know I can use a percent volatility to calculate my position size! I hadn’t heard of it before reading your article. Thank you.
My question is how to account for currency differences to calculate risk and therefore position size if I am investing across various markets in different countries? For example one trade may be taken in US$, another in AU$, and a third in CAD$.
Brilliant – I am glad you have discovered this now! For trading in other currencies you need to equate the risk back to your home currency – Say you want to calculate 0.5% risk per trade and your home currency is AUD but your trade will be in USD. First calculate 0.5% of your account in AUD… then convert that amount to USD, then size the trade.
Quite a lot to take in with this article. I tend to use percent of equity model more often but have recently seen a few people use ATR for stop loss (specifically in forex). I like how your articles have the theory behind the topic, but also use real numbers and equations so that it is easy for us to apply the information to our own trading.
I have multiple retirement accounts and taxable brokerage accounts. How do you decide what percentage of your portfolio you use for active trading vs. long term holds? Is it strictly a personal decision?
Thanks for your comment Jenn – I use percent equity for some systems and percent risk (ATR based) for others depending on which performs best with the strategy. As for the percentage of your portfolio for active trading vs long term holds that really is a personal decision. I suppose you could use the broader market return as a proxy for long term holds and add the index to your capital allocation spreadsheet along with your trading systems and work out the percentage you are most comfortable by treating your buy and hold like a system and figuring out what percentage works best. Since I don’t have any buy and hold I haven’t had to do this. Another alternative is for you to just select a percentage that you are comfortable with. I don’t think there is a single right answer in this case unfortunately.
Really interesting. A very detailed analysis.
One comment though. When you explain a gap as one of the reasons for choosing Percent vs Percent risk sizing for fight stop loss cases, is it because the gap causes the to sell below the stop loss by an unknown ammount since in that “gap” scenario, stop loss is not defining the exit price? Otherwise, if gap did not exist both methods shouldn´t be similar?
Great question Alberto. The problem is when using risk based position sizing you can end up with a large position size if you have a tight stop loss (eg if the volatility is very low), and then a gap against you would cause you to lose a lot more than expected because you exit at the price after the gap which is worse than your stop loss level (overnight gap). With percent of equity position sizing the width of the stop loss has no impact so you can’t get the situation where volatility contracts causing a large position size and then if there is a gap it causes a large loss. I still use both models, however I am careful to ensure my stops aren’t too tight with the percent risk model.
An insightful piece, i would read this over again better understanding and eventual applications, thanks. Would any of the position sizing methods have performed better with smaller accounts?
Thank you Fabian. I would think that the right position size is independent of the account size unless you have a minimum trade size for the markets you are trading (For example in Australia on the ASX you can only buy a minimum of $500 worth of a stock). In this situation percent of equity is easier to manage. Other than this the position sizing model is not determined by the account size it is more related to the particular strategy and what works best for it.
Hi Adrian, That was a very interesting article. I used a 3ATR stop for some time but found I was often stopped out too early in the trade. I liked your discussion around the worst single trade in the back test and the fact that you need to be confident that the system can survive and still profit if this trade arose at some point in the future. Also, how I need to make sure that my risk per trade takes into account this scenario. My question is due you arrive at the best position sizing calculator for the system under consideration through optimisation in the back testing?
Very informative article. This goes back to our discussion on expectancy. If I have a system that wins 80% of the time with small percentage wins I can have a higher percent risk on the loss side and vice versa as long as I account for the largest loss encountered during my backtest. For me it has been very helpful to start tying these things together to build/optimize an overall plan. I have a couple systems that I am testing and this information will be vital in determining if and how to deploy these.
Looking forward to learning more.
Great insights Chris – thank you for taking the time to share!
Hope you trading is going well
Adrian
Really great article.
Wondering have you considered some ideas which would negate the idea of a gap down below your stop? I assume this would change your allocation models.
For example:
1. Using a guaranteed stop loss.
2. Trading FX majors which really don’t gap.
3. Using options as a hedge.
Thanks Adrian.
Hi Tim,
Thanks for your great comment – love it!
Here are my thoughts:
1. Guaranteed Stops can be expensive, and when I looked at it in the past (for stocks, which I trade predominantly), the additional cost of the guaranteed stop allocated to every trade ended up being more expensive than the occasional cost of a gap through my stops. This may have changed over time but I have not revisited this in quite a few years. This just comes down to a cost benefit analysis.
2. I trade stocks, but the same idea applies – trading more liquid instruments leads to less gaps (this is good). In the stock space though, often the larger moves take place in the less liquid stocks, so if you only trade the most liquid stocks then you can miss out on these moves… this is also a cost benefit type analysis. Small position sizes in the small cap stocks allows you to catch some big moves without a large risk to your account. This is not for everyone obviously – there are many different ways to trade and configure these tradeoffs.
3. Yes this can also be done… hedging is a cost and the benefit needs to be weighed up against the cost of the hedge. I generally don’t hedge as I instead have different strategies that profit from different markets / timefames / profit drivers / directions. Others prefer to hedge.
My approach really boils down to – keep it simple with a broadly diversified portfolio of trading systems covering different strategies / markets / timeframes and keep position sizes small.
Hope that all makes sense?
Adrian
Hi Adrian, that’s a great article. Well explained and a topic dear to my heart. Position sizing is so important and not explained often enough. I read all the article and all the comments and can see many got a lot from it.
Cheers. The Zen Trader.
Hi Peter,
So great to have you here and I am glad you enjoyed the article. Thank you for taking the time to post a comment – I do love the interaction 🙂
Adrian